Toxicology Quizzes
Module One - Test Your Knowledge Quiz
1. Which of these groups is usually designated as one of the most sensitive sub-populations for exposures to toxic substances?
a. Adult women
b. Infants
c. Adult men
d. Adolescents
2. You have worked at a chemical facility for 10 years. The facility does not require protective equipment, and you have developed a number of serious health affects in the last 7 years. You are possibly experiencing what type of exposure?
a. Chronic
b. Acute
3. You are worried about contamination of vegetables grown in contaminated soils. What type of toxicologist would you contact?
a. Descriptive
b. Environmental
c. Regulatory
d. Food
4. You are concerned about risks associated with growing vegetables in soil with high lead and arsenic concentrations. You are speaking of what type of substance?
a. Toxin
b. Toxicant
5. The larger the amount of exposure and the greater the dose, the greater the observed response, or effect.
a. True
b. False
6. What type of toxicologist takes samples of your blood, urine and hair for testing?
a. Descriptive
b. Analytical
c. Mechanistic
d. Forensic
7. Toxic agents can be classified in terms of their physical state, their effects, and their source.
a. True
b. False
8. Which agency deals with the health effects that may occur from environmental exposure to toxic chemicals?
a. The Environmental Protection Agency
b. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
c. The Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry
d. The Nuclear Regulatory Commission
9. Which database has information on emergency handling procedures, environmental data, regulatory status and human exposure?
a. TOXNET
b. HazDat
c. IRIS
d. CHEMTREC
10. HazDat contains information on hazardous substances found at NPL and non-NPL waste sites, and on emergency events.
a. True
b. False
11. The no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL) is the same as the no effect level (NEL).
a. True
b. False
12. The term toxicant is used when talking about toxic substances that are produced by or are a by-product of human-made activities.
a. True 1. Name the four types of environments discussed in this module. a. 2. Which of the following is NOT a factor affecting inhalation of toxic substances? a. Concentration of toxic substance in the air 3. Chronic exposure is classified as an exposure to a chemical or other substance for a period of one year or more. a. True 4. Biotransformation occurs when a substance enters the body in one area and moves to another. a. True 5. Which of the following is not a type of exposure? a. Long-Term Exposure 6. The protective barriers for the inner environment are the__________ , __________, and the __________ 1. Which of the following is NOT a step in the Risk Assessment Process? a. Hazard identification 2. Epidemiology is the study of causative factors associated with the occurrence and number of cases of disease and illness in a specific population. a. True 3. Exposure tells the toxicologist what dose causes a "response" usually illness or death, in the test animal. a. True 4. What activities should be conducted during the hazard identification step of the risk assessment? a. Identifying the substance name 5. Prospective epidemiological studies gather information from the past. a. True 6. The exposure assessment step in the risk assessment process identifies all EXCEPT which of the following? a. Frequency of exposure 7. Susceptible populations that may be more at risk for illness than others includes the following EXCEPT: a. Young children Divide the participants into small groups. Have them perform a mock risk assessment on an environmental issue or contaminant of concern to them. To keep the process simple, inform the participants that they are to perform this activity in the manner described below. The four steps in the Risk Assessment process are: The Risk Assessment asks five basic questions, which the participants must answer: 1. What are some effects from arsenic exposure? 2. What form of mercury is the most toxic? 3. List some solvents you may use in the home. 4. List the different classes of pesticides. 5. How does carbon monoxide affect the body? 6. What are some sources of ozone? 7. List the different outdoor air pollutants discussed in the Module. 1. Which of these groups is usually designated as one of the most sensitive sub-populations for exposures to toxic substances? a. Adult women 2. You have worked at a chemical facility for 10 years. The facility does not require protective equipment, and you have developed a number of serious health effects in the last 7 years. You are possibly experiencing what type of exposure? a. Chronic 3. You are worried about contamination of vegetables grown in contaminated soils. What type of toxicologist would you contact? a. Descriptive 4. You are concerned about the risks associated with growing vegetables in soil with naturally high lead and arsenic concentrations. You are speaking of what type of substance? a. Toxin 5. The larger the amount of exposure and the greater the dose, the greater the observed response, or effect. a. True 6. What type of toxicologist takes samples of blood, urine or hair for testing? a. Descriptive 7. Toxic agents can be classified in terms of their physical state, their effects, and their source. a. True 8. Which agency deals with the health effects that may occur from environmental exposure to toxic chemicals? a. The Environmental Protection Agency 9. Which database has information on emergency handling procedures, environmental data, regulatory status and human exposure? a. TOXNET 10. HazDat contains information on hazardous substances found at NPL and non-NPL waste sites, and on emergency events. a. True 11. The no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL) is also known as the no effect level (NEL). a. True 12. The term toxicant is used when talking about toxic substances that are produced by or are a by-product of human-made activities. a. True Word Scramble (1) skin QUICK MATCHING Match the routes of exposure with the correct way for the hazard to enter the body. A. Absorption _A_ Skin 2. Epidemiology is the study of causative factors associated with the occurrence and number of cases of disease and illness in a specific population. a. True 3. Exposure tells the toxicologist what dose causes a "response" usually illness or death, in the test animal. a. True 4. What activities should be conducted during the hazard identification step of the risk assessment? a. Identifying the substance name 5. Prospective epidemiological studies gather information from the past. a. True 6. The exposure assessment step in the risk assessment process identifies all EXCEPT which of the following? a. Frequency of exposure 7. Susceptible populations that may be more at risk for illness than others includes the following EXCEPT: a. Young children Module IV - Survey of Toxic Substances Test Your Knowledge Quiz Answers 1. What are some effects from arsenic exposure? 2. What form of mercury is the most toxic? 3. List some solvents you may use in the home. 4. List the different classes of pesticides. 5. How does carbon monoxide affect the body? 6. What are some sources of ozone? 7. List the different outdoor air pollutants discussed in the Module.
b. False
Module One - Activity Lab
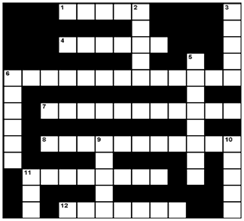
Puzzle Questions
Across
1 toxic substances produced naturally
4 contains information on hazardous substances found at NPL and non-NPL sites
6 the dose or exposure level below which the harmful or adverse effects of a substance are not seen in a population
7 the differences between two or more persons in the level of their response to exposure
8 implements regulations that control and abate air emissions from stationary and mobile sources
11 the act of coming into contact with a hazardous substance
12 long-term exposure
Down
2 no observed adverse effect level
3 short-term exposure, usually less than 24 hours
5 any chemical that can injure or kill humans, animals, or plants: a poison
6 toxicology data network
9 examines the health effects from exposure to contaminants at NPL and non-NPL sites
10 poisonous or deadly effects on the body by inhalation, ingestion, absorption, or contact with a chemical
11 deals with the environmental impacts of exposure to hazardous substances
Module Two - Test Your Knowledge Quiz
b.
c.
d.
b. Speed of the wind
c. Length of exposure
d. Size of toxic particle
b. False
b. False
b. Chronic Exposure
c. Short-Term Exposure
d. Small Exposure
Module Three - Test Your Knowledge Quiz
b. Hazard evaluation or dose-response assessment
c. Exposure dose
d. Risk characterization
b. False
b. False
b. Describing the physical/chemical properties of the toxic substances
c. Identifying the sources of toxicity information
d. Identifying the exposure pathway
e. All of the above
b. False
b. Type of chemical exposure
c. Length of time of exposure
d. Route of exposure
e. The amount of exposure
b. Older adults
c. Teenagers
d. Women of Childbearing Age
Module Three - Activity Lab
Module Four - Test Your Knowledge Quiz
For More quizzes and answers please click on this link.
http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/training/toxmanual/index.html.
Answer Key
Module I Test Your Knowledge Quiz Answers
b. Infants
c. Adult men
d. Adolescents
b. Acute
b. Environmental
c. Regulatory
d. Food
b. Toxicant
b. False
b. Analytical
c. Mechanistic
d. Forensic
b. False
b. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
c. The Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry
d. The Nuclear Regulatory Commission
b. HazDat
c. IRIS
d. MEDTREC
b. False
b. False
b. FalseModule I - Toxicology Puzzle Solution
Module II - Routes of Exposure Word Scramble and Matching Solution
(2) intestine
(3) nose
(4) eye
(5) mouth
(6) ambient
(7) macrophages
(8) environment
(9) biological
(10) gaseous
(11) soil
(12) air
(13) water
(14) food
(15) dermis
(16) inhalation
(17) route
(18) media
(19) groundwater
(20) food chain
B. Ingestion
C. Inhalation
_A_ Eye
_B_ Mouth
_B_ IntestineModule III - Risk Assessment Test Your Knowledge Quiz Answers
1. Which of the following is NOT a step in the Risk Assessment Process?
a. Hazard identification
b. Hazard evaluation or dose-response assessment
c. Exposure dose
d. Risk characterization
b. False
b. False
b. Describing the physical/chemical properties of the toxic substances
c. Identifying the sources of toxicity information
d. Identifying the exposure pathway
e. All of the above
b. False
b. Type of chemical exposure
c. Length of time of exposure
d. Route of exposure
e. Calculation of the amount of exposure
b. Older adults
c. Teenagers
d. Women of Childbearing Age
Death, fever, anorexia, and liver enlargement are some of the effects listed in the module.
Methyl mercury is the most toxic form of mercury.
Participant answers
Insecticides, Herbicides, Fungicides, Fumigants, Rodenticides
Decreases amount of oxygen available to the body. Also causes headache, shortness of breath, nausea, irritability, increased respiration, chest pain, impaired judgement, and fainting.
Lightning, high voltage electrical equipment, and air- and water-purifying devices are some sources of ozone.
Carbon monoxide, Sulfur oxides, Ozone, Nitrogen oxides, Particulates
=======================================================================================
1. A 16-year-old female presents to the emergency department with agitation, confusion, tremors, and hyperreflexia. The patient is currently treated for depression. Fluoxetine (Prozac) was adjusted yesterday prior to presentation because of increased depressive episodes. Her mother is currently taking thioridazine (Mellaril) for psychosis. What is the most likely cause of the patient's current condition?
a. Fluoxetine (Prozac)
b. Acute ingestion of Thioridazine
c. Mania
d. MDMA (ecstasy)
e. Psychotic break with paranoia
2. The American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention recommends the following with regard to accidental home ingestions:
a. Keep a 1 oz bottle of syrup of ipecac for acute ingestions and call Poison Control Center prior to administration.
b. Give activated charcoal for acute ingestion.
c. Do not give syrup of ipecac, but call the Poison Control Center for all suspected toxic exposures.
d. A and B
3. A 15-year-old teenage girl presents to the emergency department after her mother reports that her daughter has been having nausea and vomiting for the last 3 hours. The patient is scared and reports to taking a mouth full of acetaminophen. Her current blood level of acetaminophen is pending, but liver transaminases are elevated. What is the next most appropriate step in the treatment of this patient?
a. Gastric lavage
b. Administer activated charcoal
c. Administer N-acetylcysteine (NAC)
d. Psychiatric consultation
4. A 7-year-old male, whose father is a migrant worker, presents to the emergency department with acute onset of vomiting, diarrhea, salivation, and urinary incontinence. On physical exam, the child is anxious and restless with a heart rate 65 beats/min. Lung exam is significant for wheezing and his pupils are dilated. What is the mechanism of action for the antidotes that should be administered to this patient? (Select as many answers as are correct.)
a. Competitive antagonist of acetylcholine at the muscarinic receptors.
b. Selective competitive agonist of acetylcholine at the nicotinic receptors
c. Cleavage of the phosphate moiety from the phosphorylated enzyme and organophosphate complex.
d. Irreversible antagonist of acetylcholine at the nicotinic receptors
5. A 13-year-old female was prescribed nitrofurantoin and phenazopyridine for a urinary tract infection. She presented to the emergency department 3 days later for dizziness and cyanosis. Methylene blue was administered and had no effect on the patient's condition. What are possible causes of the patient's persistent cyanosis?
a. NAPPH methemoglobin reductase deficiency
b. G6PD deficiency
c. Sulfhemoglobinemia secondary to phenazopyridine
d. All of the above
e. None of the above
6. Which of the following cardiac effects are seen with TCA overdose?
a. QRS prolongation, atrioventricular block
b. Sinus tachycardia
c. Ventricular tachycardia, Monomorphic
d. Torsades de Pointes
e. All of the above
f. A, B, C, but not D
7. A 16-year-old male is brought to the emergency department by his friends after they found him unresponsive. Physical exam is significant for a Glasgow scale of 4, respiratory rate of 7, and pupils constricted. What is the next most appropriate step in his treatment?
a. Administer thiamine and dextrose
b. Begin ventilating the patient, intubate if necessary
c. Administer naloxone
d. Perform a gastric lavage
e. All of the above
8. Of the following statements concerning sniffers and toxic inhalation, which are TRUE?
a. Sudden stress, hypercapnea, hypokalemia, and hypoxia predisposes a sniffer to greater cardiac toxicity
b. Methylene chloride, found in various paint strippers, is metabolized rapidly to glyceraldehyde, which has toxic effects on the body
c. The most common cause of death after sniffing is hypoxia and direct toxicity to the lungs.
d. Benzene can cause aplastic anemia
9. A 4-year-old female was playing in the garage with her older brother when she developed an unsteady gait, ataxia, myoclonic jerks, and started vomiting. Her mother noted a green puddle of automotive fluid on the floor where the children were playing and immediately took her to the local emergency room where she was evaluated. Which metabolite of the ingested agent causes tissue injury?
a. Glycolic Acid
b. Glycoaldehyde
c. Oxalate
d. Glyceraldehyde
10. A 16-year-old male kennel worker at a local veterinary clinic presented to the emergency department with a history of confusion, slurred speech, and unsteady gait. The patient reportedly was fine when he went to school and work today. While in the emergency department, the patient became violent and had to be restrained. Physical exam was remarkable for vertical nystagmus, tachycardia, and drooling. Which of the following might have been the ingested agent? (Hint: there may be more than one correct answer.)
a. Angel Dust (Phencyclidine or PCP)
b. Telazol- (Tiletamine and Zolazepam), a veterinary anesthetic
c. Crystal Methamphetamine
d. Diazepam
11. Gastric lavage is contraindicated in each of the following ingestions except:
a. Liquid plumber
b. Gasoline
c. Tricyclic Antidepressant (TCA)
d. Clonidine patches
e. None of the above
12. Which of the following statements regarding arsenic poisoning are TRUE (there may be more than one)?
a. Mees lines are white lines on the fingernails indicating chronic arsenic poisoning
b. If exposed to arsenic gas, the most common presenting symptoms are abdominal pain, hematuria, and jaundice along with diminished mental status.
c. Arsenic impairs cellular respiration by inhibiting mitochondrial enzymes and uncoupling oxidative phosphorylation and can also block pyruvate dehydrogenase.
d. Arsenic can be found in herbicides, fungicides, wood preservatives, and desiccants.
13. An 8-year-old girl was playing near a factory dumpsite when she developed the following signs and symptoms: rotten egg smell, keratoconjuctivitis, and upper airway irritation with coughing and confusion. Her mother also noticed that her silver earrings and charm bracelet were blackened. What is the most likely diagnosis?
a. Arsenic exposure
b. Cyanide exposure
c. Hydrogen Sulfide exposure
d. Carbon Monoxide exposure
1. These are major routes of drug administration, EXCEPT:
a. Oral
b. Intravenous
c. Intramuscular
d. Rectal
e. None of the abovr
2. This is the major carrier protein of drugs in the circulation:
a. Globulin
b. Albumin
c. TBPA
d. Ferritin
e. None of the above
3. The therapeutic range of a drug is the blood level of the drug that;
a. Cures the disease
b. Gives no side effects
c. Determines the extent of the condition
d. Allows maximum exposure of the patient to the drug
e. None of the above
4. The following are aminoglycosides, EXCEPT:
a. Digoxin
b. Procainamide
c. Quinidine
d. Theohpylline
e. None of the above
5. Trinder’s reagent is for the quantitation of:
a. Acetaminophen
b. Phenobarbital
c. Salicylate
d. Theophylline
e. None of the above
6. The drug dosage given to patients with this condition should be lower than the
therapeutic range:
a. Liver cirrhosis
b. Pneumonia
c. Septicemia
d. Viral influenza
e. None of the above
7. Isopropyl alcohol should NOT be used as a sterilizing agent for ethanol analysis,
because:
a. It may falsely increase obtained values
b. It may falsely decrease obtained values
c. It interferes with the reaction
d. It reacts with the reagents for the determination
e. None of the above
8. The product measured in alcohol determination is:
a. acetylsalicylate
b. LDH
c. NAD+
d. NADH
e. acetaldehyde
9. The major metabolite of marijuana is:
a. heroine
b. benzoylecgonine
c. 9 delta THC
d. phencyclidine
10. The major metabolite of morphine is:
1. Which of the following poisonous plants is also known as be-still tree in common parlance?
- Abrus precatorius
- Croton tiglium
- Cerbera thevetia
- Capsicum annum
2. Which of the following poisons has the chemical formula C2H2FNaO2?
- Sodium fluoroacetic Acid
- Sodium fluoroacetate
- Compound 1080
- All of the above
3. Which of the following properties should an ideal homicidal poison have?
- It should be colorless
- It should be tasteless
- It should be odorless
- All of the above
4. In 1945, in Japan a disease known as “Itai-Itai disease” spread. This was due to a poison. Which was it?
- Iodine
- Barium
- Selenium
- Cadmium
5. Why is strychnine not an ideal choice as a homicidal poison?
- It is a very costly poison
- It can be detected very easily in the body organs with a simple chemical test
- It is extremely bitter in taste
- It has to be given in very high dose to be effective
6. Hepatoma, a kind of liver cancer can be produced by a poison. Can you identify it from the list given below?
- Diesel fumes
- Aflatoxin
- Arsine gas
- Vanadium
7. Which of the following poisons was often known as the “inheritance powder”?
- arsenic
- Nux vomica
- lead tetroxide
- mercuric chloride
8. Which is the following poisons is also known as the Lunar caustic?
- Aqua regia
- Nitric Acid
- Sodium hydroxide
- Silver nitrate
9. Which of the following poisons was often referred to as the “king of poisons”?
- Nux vomica
- arsenic
- Hydrocyanic acid
- potassium cyanide
10. Which of the following is closest to being an ideal suicidal poison?
- Sulphuric acid
- Caustic Soda
- Barbiturates
- Nitric acid
1. The venomous animal Muraena helena has how many legs?
none
two
four
six
eight
2. Which of the following is NOT a chlorinated hydrocarbon insecticide?
lindane
DDT
dieldrin
mirex
cabaryl
3. From which of the following would you be most likely to obtain protoanemonin?
a tropical fish
a marine alga
a terrestrial plant
an insect
a mushroom
4. Which of the following is NOT true about selenium poisoning?
Some pasture plants accumulate selenium.
selenium tends to replace sulfur in amino acids.
Selenium may cause deformities in waterfowl.
Horses with chronic selenium poisoning may have deformed hooves.
Selenium poisoning is unlikely on arid, alkaline soils
5. Which of these is an INCORRECT pairing of neurological poison and mechanism?
strychine: inhibition of glycine in the CNS
nitrofurazone: inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation in the CNS
amphetamines: inhibition of catecholamine release in the CNS
metaldehyde: decrease of 5-hydroxytryptamine and GABA in the CNS
fluoroacetate: inhibition of aconitate hydratase in the TCA cycle in the CNS
6. Which of these is an INCORRECT pairing of plant and toxic action?
Cicuta maculata: seizures
Berteroa incana: cardiac failure
Cassia occidentalis: muscle degeneration
Halogeton glomeratus: kidney damage
Phytolacca americana: gastrointestinal irritation
1. The word Toxicology comes from
a. An Egyptian word meaning "killing shrewdly"
b. A Roman word meaning "poisons"
c. A Greek word toxon meaning a bow
d. A Sanskrit word meaning "bitter substance"
2. Which of the following poisoners is usually regarded as the the greatest poisoner of all time?
a. Catherine de Médici
b. Toffana
c. Marquise de Brinvilliers
d. Mary Ann Cotton
3. Which of the following queens was so barbaric that she is reputed to have tested and studied the effects of various poisons on the poor and the sick?
a. Queen Elizabeth
b. Mary Queen of Scots
c. Noor Jehan
d. Catherine de Medici
4. This woman was an expert in poisons. She reputedly developed a flourishing trade in selling poisons to wives who wished to rid themselves of their husbands! Who was she?.
a. Catherine Deshayes
b. Marquise de Brinvilliers
c. Mary Ann Cotton
d. Catherine de Médici
5. He injected fruit trees with potassium cyanide. The idea was that it would rise up along the conducting system and be incorporated in the fruits. The poisoned fruits could then be given to rivals to kill them! Who was this innovative person?
a. Aristotle
b. Leonardo da Vinci
c. Galen
d. Paracelsus
6. One of the most ancient medical documents, the Ebers Papyrus, mentions several poisons. The Ebers papyrus is dated
a. about 1550 BC
b. about 2550 BC
c. about 3550 BC
d. about 4550 BC
7. He wrote two treatises, which are supposed to be the most ancient works devoted entirely to poisons. Who was he?
a. Aristotle
b. Charak
c. Hippocrates
d. Nicander of Colophon
8. In the past, even nations were involved in poisoning their rivals. In which of the following cities was there was a Council who met regularly to arrange poisoning for the State?
a. Paris
b. Athens
c. Venice
d. Cuzco
9. Which poison was given to Socrates?
a. Arsenic
b. Hemlock
c. Snake Venom
d. Powdered pieces of glass
10. These persons used a secret poison called La Cantarella to kill their rivals. Who were they?
a. Ancient Greeks
b. The children of a French King of 12th Century
c. Allied powers during World War I
d. The children of a former Pope
1. Which of the following salts of arsenic is known in Hindi as Sankhya or Somalkhar?
- Arsenic trichloride
- Arsenic oxide
- Arsenic hexafluoride
- Arsphenamine
2. Which of the following scientists first synthesized the above deadly poison?
- Hippocrates
- Charak
- Avicenna
- Geber
3. Which natural disease does a person seem to suffer from when he is given arsenic?
- Diphtheria
- Cerebral palsy
- Cholera
- Heart disease
4. Which of the following facts about strychnine is correct?
- It is very difficult to administer it with a homicidal intent
- It is a very good homicidal poison
- It is very popular as a suicidal poison
- It is the only sweet poison known to man
5. Which property of arsenic makes it a very poor homicidal poison?
- It is a coloured salt
- It tastes very bitter, so potential victim would spit it out immediately
- It is very costly, costing much more than gold weight for weight
- It can be detected years after death, in the bones of the victim
6. Which of the following tests is used to detect arsenic?
- Meixner test
- Marsh Test
- Marquis Test
- Melzer’s Test
7. Which of the following is the main organ to suffer in chronic arsenic poisoning?
- lungs
- uterus
- prostate
- skin
8. The first test to detect arsenic in human body was detected in......
- prehistoric times
- early 12th Century
- 1752
- 1836
9. Soon after the test for detecting arsenic in human body was discovered (see question 6 above), it was used in a celebrated poisoning case. Who was the poisoner?
- Mary Blandy
- Marie Lafarge
- Charles Lafarge
- Catherine Deshayes
10. Karl Wilhelm Scheele remains an important chemist involved in the development of a useful test to detect arsenic in human body (see question 6 above), which ultimately brought arsenic in disfavour as a homicidal poison. What exactly did Scheele do?
- He was a teacher of the chemist who developed this test
- He was the first to detect arsenic by Gas Liquid chromatograph
- He found he could change arsenious oxide to arsenious acid by treating it with nitric acid. This was an important precursor to the development of the test
- He was the first to discover that squirrels had the capacity to smell arsenic. This simple discovery brought about a revolution in the discovery of arsenic in homicidal poisonings.
1. At ordinary temperature and pressure, methyl bromide is a
- hard rocky solid
- jelly like solid
- liquid
- gas
2. In high concentrations, how does methyl bromide smell?
- sickly sweet
- garlicky
- strongly pungent
- musty and acrid
3. Which of the following is NOT a genuine use of methyl bromide?
- used as a fumigant and insecticide
- used for making explosives
- used as a refrigerant
- used in dye industry
4. Methyl bromide is known by all of the following names except
- Dibromomethane
- bromomethane
- Embafume
- iscobrome
5. Excretion of methyl chloride occurs chiefly through
- feces
- sweat
- Lungs
- Kidneys
6. Normal bromide levels in adults are about 0.3-0.4 mg/dL. In death due to inorganic bromide ingestions such as sodium or potassium bromide, the blood levels must rise to about
- 30 mg/dl
- 300 mg/dl
- 3g/dl
- 30g/dl
7. Methyl bromide causes death by
- preventing glycolysis to take place
- methylation of sulphydryl groups of several important enzymes
- increasing bromine levels in blood
- a complex phenomenon known as “bromism”
8. In deaths due to methyl bromide the most important autopsy findings are to be found in ....
- parathyroid glands
- Intestines and caecum
- brain
- testes in the males and ovaries in the females
9. What is the color of pure methyl bromide?
- light blue
- yellow
- green
- colorless
10. In deaths due to methyl bromide, the blood levels of bromide are in the range of
- 8-9 mg/dL
- 80-90 mg/dL
- 8-9 g/dL
- 80-90 g/dL
1-Sources of quizzes.txt
2-variant 1.txt
3-Toxicology Quizzes.docx
4-Variant 2.txt
5-Varient 4.txt
6-Varient 3.txt
7-Varient 6.txt
8-Varient 5.txt
9-Varient 7.txt
10-Varient 8.txt
11-Varient.txt
=======================-===============================================================
Free University Lectures Online
http://www.4shared.com/document/_kCwBcGJ/1_Introduction.html
http://www.4shared.com/document/226VeA2D/1Vibration_disease_Dr_Stoyneva.html
http://www.4shared.com/document/EJoEG5_t/4_Musculoskeletal_Dr_Stoyneva.html
http://www.4shared.com/document/U9mh4i6j/6_EMF_English.html
http://www.4shared.com/document/viWURfKw/Ch17-GI-1.html
1- http://www.4shared.com/file/223950015/f408e00/1_Introduction.html
2-http://www.4shared.com/file/223950416/91407766/1Vibration_disease_Dr_Stoyneva.html
3-http://www.agls.uidaho.edu/etox/lectures.htm
4-http://divisions.aspet.org/toxicology/lectures_on_demand.htm
5-www.101med.com/index.php?option=com_docman
6- http://xnet.rrc.mb.ca/davidb/environm.htm
More and more universities are putting videos of their lectures online. Here are some that I know of.
- University of California Berkeley
- Webcast page
- Purdue University
- Boilercast page
- University of Washington
- Classroom Support page
- U. of Utah
- Courses
- Princeton University
- University Channel
- University of Texas
- World Lecture Hall
- WGBH Boston
- Their archive
- Georgetown Law
- Their webcast page
- LecturesArchive.com
- Link
- Massachusetts Inst. of Technology
- MIT OpenCourseWare
MITWorld
Audio-visual links - University of Idaho
- Food Toxicology lectures
- University of California Los Angeles (UCLA)
- Office of instructional development
- Yale
- Course list
Ancient Greek history - France
- Webcasts in French
- US Department of Energy
- Save Energy Now series.
- U. of Utah
- Some mp3s of courses